Later on in Meroë, women had a greater role in politics. Earlier, with Egyptian influence, their role was less. (help add info)
Know gender roles in each of the classical civilizations— what gender role did women have in the Nubian civilization?
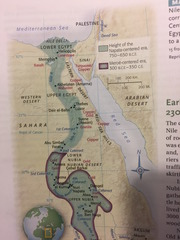
Nubia (3100 BCE - 350 CE)
a thousand mile stretch of Nile Valley lying between *Aswan* and *Khartoum*, in modern south Egypt and north Sudan. only continuously inhabited territory connecting sub-Saharan Africa with North Africa. Corridor for trade between tropical Africa and Mediterranean, possessing gold, copper, and semiprecious stones (natural wealth)
Gold
Egypt had a hunger for Nubian _______, which helped lead to the arising of a complex civilization
Historians no longer think that Nubia imitated Egypt (which wanted Nubian gold). Nubia was influenced by Egypt and sub-Saharan Africa, a result of its tremendous trade positioning
Was Nubia a civilization that simply imitated Egypt? If not, name Nubia's influences
Nile
Like the Egyptians, the Nubians were centered around this geographical feature. The __________ flowed through rocky desert, grassland, and a fertile plain.
Irrigation (from the river)
________ was essential for agriculture in Nubia due to the severely hot climate and the dry north. Mesopotamia relied on this, but Egypt and the Indus Rivery Valley civ. did not.
Cataracts
Natural barriers formed by large boulders and rapids. Obstructed boat traffic. Caravans skirted (went around) the river
Trade through Nubia was evident due to ivory and ebony wood Egyptian crafts found before 3000 BCE (natural resources from tropical Africa). Nubia was between sub
Saharan/tropical Africa and Egyptian (add more plz) - How did trade affect Nubia (please add more to my bad answer)
Aswan (Syrene)
A city that was the Old Kingdom's southern limit of Egyptian control. Just north of First Cataract
Gold, incense, ebony, ivory, slaves, exotic animals. From tropical Africa. Great rewards resulted. (*what did Egyptians trade, do you know*)
Why did the Egyptians send donkey caravans south? What did they trade for? (this was dangerous because of negotiations with local Nubian chiefs)
Middle Kingdom (2040-1640 BCE)
Kingdom period in Egypt when they more aggressively pursued Nubia. Control gold mines in desert east of Nile. During Middle Kingdom = peaceable relations, no little interaction between Egypt and *indigenous* northern Nubians w/ Old farming/herding ways
south of 2nd cataract
Where Egyptians erected mud-brick forts on islands and riverbanks in order to regulate flow of trade and to protect southern border from Nubians and nomadic desert raiders
Kush
Egyptian name for Nubia, the region alongside the Nile Rive south of Egypt, where an indigenous kingdom with its own distinctive institutions and cultural traditions arose beginning in the early second millennium BCE
Kerma
capital of the kingdom of Kush
In 1750 BCE, they built walls and monumental brick structures. Sacrificed dozens/hundreds of servants/wives w/ king burials. Belief in afterlife where attendants/possessions = useful. Put rich objects. Show wealth/power of rulers of Kush
Name the religious structure of Kush before Egyptian dominiation (specifically, their afterlife before Egyptian domination) (fun fact = Kushites wrote *high quality poetry*)
Gebel Barkal
"Holy Mountain" of Nubia, had temples. Napata, capital of Egyptian Nubia was near here
New Kingdom (1532-1070 circa BCE)
An expansionist period of the Egyptians, they went further into Nubia, destroyed Kush + Kerma, and extended their frontier to the Fourth Cataract. Led to the assimilation of the Nubian peoples. They dominated Nubia for 500 years
Overseer of Southern Lands (King's Son of Kush)
ruler of Nubia from new capital Napata. Denotes force.
Less resistance from Nubians, easy assimilation of culture
Why put Napata capital near Gebel Barkal?
Amon
Egyptian god respected by Nubians, depicted with head of ram (possibly a blend between Amon and a Nubian ram deity). Nubians now modeled their culture after Egypt.
(Kingdom of) Meroë (800 BCE
350 CE) - capital of flourishing kingdom in southern Nubia from fourth century BCE to fourth century CE. Nubia shows more independence from Egypt and sub-Saharan Africa
Nubia (712 to 660 BCE)
The kings of _____ ruled all of Egypt in the Twenty-fifth Dynasty (712 to 660 BCE). Conducted Egyptian ruler manners. Egyptian customs. Royal titles. Traditional costume. Buried according to Egyptian custom. Artistic + cultural renaissance. Building on monumental scale. Egyptian art, architecture, religion
Memphis
capital of the Old Kingdom (of Egypt) and the capital of Nubian Egyptian dominance (during Twenty-fifth Dynasty (712 to 660 BCE))
Thebes
New Kingdom capital that became residence of celibate (chastity) female member of king's family, called "God's wife of Amon"
Disastrous mistake in 701 BCE by Nubians
attempted to help struggling Palestinian rulers against Assyrian Empire. Assyrians invaded Egypt, drove Nubian monarchs back to southern domain. By 660 BCE - Napata became the capital again
Shawabti figurines
Religious figurines used in Nubia because of Egyptian influence. *Egyptians wielded incredible influence on Nubia*
↑ agriculture/trade, good for economy
Why was the new capital of Nubia situated in Meroë (by fourth century BCE)?
Meroë
Kingdom of ________, worshipped Amon/Isis as well as Nubian deities (e.g. Apademak). Undeciphered symbols (not hieroglyphs) for Meroitic language. Art combined Egyptian, Greco-Roman, indigenous traditions. Also a city. New kingdom of Nubia
sub-Saharan Africa (help reword question
Under which civilization's (area) influence do women of royal family play an important role in politics in Meroë (help reword)
Meroë
__________ was a huge city - > square mile. Capital of a kingdom in Nubia. Fertile grasslands, trade routes. Great reservoirs to catch rainfall. *Iron smelting*. City is buried under sand today
Because much of the city is buried under the sand, archaeologists use magnetometers to detect buried structures. THey founda large palace, the temple of Amon, and a wall.
Information to know - how did archaelogists find the buried structures of Meroë
Nomads
Meroë collapsed in early fourth century, overrun by western desert _________, people who have no permanent abode. The camel coming into North Africa allowed this to happen.
They had weakened trade routes, as the Roman Empire traded with the Red Sea and Aksum instead. Also, the introduction of the camel helped the nomads take over.
Why did Meroë fall?
Aksum
rising empire in present-day Ethiopia. Romans traded with them instead
Nubia's natural wealth + location on trade route between Egypt and sub-Saharan Africa + Egyptian hunger for Nubian gold explain early rise of complex civilization there
Explain why a complex civilization in Nubia emerged.
During long periods of Egyptian domination, as well as a period in which Nubian rulers controlled Egypt, Nubian culture and technology were strongly influenced by Egyptian practices
What civilization affected Nubian culture the most?
Sub-saharan africa
During the Meroitic period, Nubia came under stronger cultural influences from ____________, as seen by the emergence of queens
Nubia's collapse in the early fourth century CE was due to shifting trade routes and attacks from desert nomads
What caused Nubia's collapse in fourth century CE?