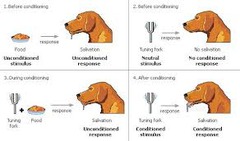















Define learning, and identify two forms of learning.Learning is a relatively permanent…
When shifting gears with a manual transmission, the clutch must be:always be…
MboteHelloNa zali malamuI am fineNa zali malamu teI am not fineBoni?How are…
UGA was chartered in…1785Classes began at UGA in…1801UGA graduated its first class…
Shanty Town Kid authorAzouz Begagshanty town kid settinglyon, second largest french city,…
compassionateKind/Understanding (adj.) My friend is very compassionate and loving, but he also…
Which of the following are likely symptoms of malware infection? (Select two.)A….
socioculturalThe ____ approach focuses on comparisons of behavior across countries as well…
Social PsychologyThe scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate…
observational learningLearning by observing others.modelPerson observed in observational learning.modelingProcess of observing and…
6.1 Summary Behaviorism focuses on…-observable aspects of learning6.1 Summary Conditioning occurs when…-a…
learning?process in which changes in behaviour arise as a result of experiences…

Hi! We can edit and customize this paper for you. Just send your request for getting no plagiarism essay
Order here