Buddhism
Belief system that started in India in the 500s BCE. Happiness can be achieved through removal of one's desires. Believers seek enlightenment and the overcoming of suffering. A path of practice and spiritual development leading to Insight into the true nature of reality.
600 BCE - 600 CE
Classical Era Time Period
Judaism
A religion that originated in the Middle East, founded by Moses. They believe that there is one God whom they covenant. A common symbol for this religion is David's Star.
Christianity
A religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus
Hinduism
Most prevalent religion in India, that integrates spiritual beliefs with daily practices and official institutions such as the caste system.
Confucianism
Emphasized education, family, peace, and justice
Daoism (Taoism)
Philosophy based on the ideas of the Chinese thinker Laozi, Who taught that people should be guided by a universal force called the Dao.
Zoroastrianism
A religion originating in ancient Iran. It centered on a single benevolent deity-Ahura Mazda, Emphasizing truth-telling, purity, and reverence for nature, the religion demanded that humans choose sides between good and evil
Torah
Sacred Book for the Jewish & Judaism
Synagogues
the building where a Jewish assembly or congregation meets for religious worship and instruction
Siddhartha Gautama
The founder of Buddhism
Vedas
Religious texts that were passed down from generation to generation of Aryans in the form of hymns, songs, prayers and rituals honoring the Aryan gods
Reincarnation
The rebirth of a soul after the body dies
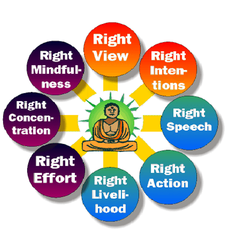
Nirvana
Union with the universal spirit; can be reached through the four noble truths and eightfold paths
Pax Romana
the period of peace that existed between nationalities within the Roman Empire
Law of Twelve Tables
the earliest code of Roman civil, criminal, and religious law
Punic wars
a series of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage from 264 BC to 146 BC. At the time, they were probably the largest wars that had ever taken place.
Constantine
was Roman Emperor from 377 - 306BC, he was the first emperor to profess Christianity and turned Rome in a Christian State
Diaspora
Scattering of Hebrews because of conquerers that spread them to other parts of the earth
Karma
A destiny that has been shaped by years of cause and effect, that is outwardly revealed by and individuals caste or station life
Eightfold path
Composed of eight steps that must be mastered one at a time
Mahabharata
Worlds longest poem that contains Hindu beliefs
Dharma
Set of duties that the individual must fulfill
Shiva
A supreme deity, the preserver
Ramayana
A poem that demonstrates the fulfillment of Dharma
Vishnu
A supreme deity, the destroyer
Paul
One of the twelve men to follow Jesus and the most responsible for the rapid growth of Christianity. Was a key Christian leader who was initially a Jewish rabbi and hostile towards Christians, but became an ardent follower.
Great Wall of China
Wall began in the Qin Dynasty
Brahmin
Priests who compiled the Vedas
Kshatriya
warriors and officials (caste system)
Vaishya
merchants, artisans, and landowners (caste system)
Shudra
peasants and laborers (caste system)
Vedic Age
Lasted from 1500 to 500 BCE, time period after the collapse of the Indus River Valley Civilization, contained the Vedas, which are religious texts
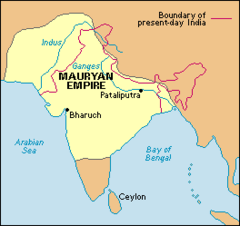
Mauryan Empire
(321-184BC) The first united Indian state, founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 324 BCE, after Alexander's defeat of weakened India; it lasted for more than 100 years, before it declined, and fell in 183 BCE.
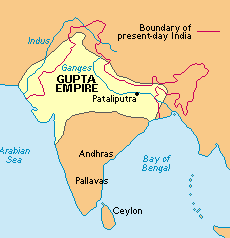
Gupta Empire
320BC-550CE, located in northern India
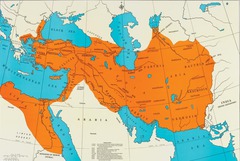
Persian Empire
Indo-Europeans who settled in present-day Iran. Defeated the Babylonians and created the largest empire in the world up to 500 BC. It stretched across Africa, the Mediterranean, Turkey, Greece, and Afghanistan. Persia was later conquered by Alexander the Great.
Qin Dynasty
Iron weapons helped army defeat other states until it controlled China, King declared himself "First Emperor"
or Shi Huangdi (ruled 221 - 210 BCE. The dynasty didn't last long but is significant in regard to the development of the Chinese state, and developed bureaucracy (it also made the Great Wall of China)
Han Dynasty
Dynasty that lasted from 206-220BC and began the official establishment of the Silk Road.
Byzantine Empire
The eastern half of the Roman Empire, which survived after the fall of the Western Empire at the end of the 5th century C.E. Its capital was Constantinople, named after the Emperor Constantine.
Mayan Civilization
Civilization of the Americas located in Central America that saw its height from 200-900 CE.
Hellenistic Synthesis
Hellenistic culture mixed with other cultures, creating cosmopolitan societies connected by trade and Greek culture
Athens and Sparta
two main city-states of Greek Empire
Legalism
Chinese philosophy developed by Han Feizi; taught that humans are naturally evil and therefore need to be ruled by harsh laws.
Mandate of Heaven
Ancient Chinese belief/theory and philosophical idea that tiān (heaven) granted emperors the right to rule based on their ability to govern well, appropriately and fairly.
Aristotle
A Greek philosopher and scientist who was interested in practically every field of human endeavor.
Socrates
First philosopher to focus on ethical questions and truth-seeking regarding human nature, understandings and relationships
Marathon
Battle in 490 BCE Greeks defeat Persia
Peloponnesian war
431-404 BCE) between Athens and Sparta. With Sparta winning, both were still majorly weakened, they were conquered by Macedonia
Triumvirate
Rule of three men holding power (in ancient Rome)
Ex: the unofficial coalition of Julius Caesar, Pompey, and Crassus in 60 BC
Four noble truths
・all of life is suffering
・all suffering is caused by desire for things that ultimately won't fulfill us
・desire can only be overcome by ending all desire
・desire can only be ended by following the eighthfold path
Boddhisatva
A person who had taken the the eightfold path and reached perfection but had delayed entering nirvana in order to help others along the way
Alexander The Great
Between 334 and 323 B.C.E. he conquered the Persian Empire, reached the Indus Valley, founded many Greek-style cities, and spread Greek culture across the Middle East.
Bureaucracy
A system of government in which most of the important decisions are made by state officials rather than by elected representatives
Ashoka
Leader of the Mauryan dynasty of India who conquered most of India but eventually gave up violence and converted to Buddhism
Chandragupta Maurya
Founder of the Mauryan Empire, first emperor to unify most of India
Chandra Gupta
Founder of the Gupta Empire
Caste System
A Hindu social class system that controlled every aspect of daily life
Athens
A democratic Greek polis who accomplished many cultural achievements, and who were constantly at war with Sparta.
Sparta
A powerful Greek military polis that was often at war with Athens. Used slaves known as helots to provide agricultural labor.
Shi Huangdi
Founder of the short-lived Qin dynasty and creator of the Chinese Empire (r. 221-210 B.C.E.). He is remembered for his ruthless conquests of rival states and standardization.
Analects
Collection of moral and social teachings of Confucius, including the concept of the Five Relationships.
Confucius
(551-479 BCE?) Chinese philosopher and writer of The Analects, a collection of moral and social teachings, including the concept of the Five Relationships. Also known as Kong Fu Zi.
Teotihuacan
(200 BCE - 750 CE) Highland Mexico, largest city, obsidian, more than 5000 structures, pop 125-200k people, large pyramids, no ball courts, no writing, city of the gods, evidence for large fires.
Zoroaster
Founder of Zoroastrianism, a religion unique to Persia.
Royal Road
Created by King Darius, a system of roads in the Persian empire stretching over 1,600 miles. It connected the vast empire and helped with communication and transportation
Mayan
2000 BCE - 1500 CE, located in Southern Mexico, and was divided into city-states each with their own kind, rural area for farming, and city area temples. They also had a fair legal system with laws and courts.
Quran
Sacred religious texts for Islam
Cyrus the Great
Extended territory from India to the Mediterranean Sea, Reached its height under Darius I (into Egypt and Macedonia) and established law code based on earlier Mesopotamian codes.