Persian Empire
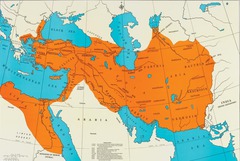
Greatest empire in the world up to 500 BCE. Spoke an Indo-European language. A multi-ethnic and multi-religious empire. Fell to Alexander the Great.
Athenian Democracy
First recorded democracy ever established. Direct democracy with juries of up to 2,500 people. Had to be an 18 year old male with Athenian parents to rule. Freedom of Speech.
Greco-Persian Wars
Two major Persian invasions of Greece, 490 and 480 B.C.E., in which the Persians were defeated on both land and sea each time.
Hellenistic era
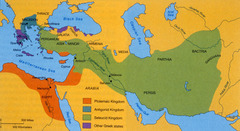
period when the Greek language and Greek ideas spread to the non-Greek peoples of southwest Asia
Alexander the Great
Between 334 and 323 B.C.E. he conquered the Persian Empire, reached the Indus Valley, founded many Greek-style cities, and spread Greek culture across the Middle East.
Augustus
The first emperor of Rome whose leadership brought about a long period of Pax Romana (Roman Peace).
pax romana
Roman Peace
A period of peace and prosperity throughout the Roman Empire, lasting from 27 B.C. to A.D. 180.
Qin Shihuangdi
(r.221-210 BCE) The first emperor of the Qin Dynasty who believed strongly in Legalism and sought to strengthen the centralized China through public works.
Trung Trac
Vietnamese nationalist and hero; along with her sister, Trung Nhi, she raised an army that drove the Chinese out of Vietnam for a short period
Han Dynasty
(202 BC - 220 AD) dynasty started by Lui Bang; a great and long-lasting rule, it discarded the harsh policies of the Qin dynasty and adopted Confucian principles; Han rulers chose officials who passed the civil service exams rather than birth; it was a time of prosperity
Mauryan Dynasty
322-185 BCE. The first state to unify most of the Indian subcontinent. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 and survived until 185 BCE. From its capitol at Pataliputra in the Ganges Valley it grew wealthy from taxes.
Ashoka
Third ruler of the Mauryan Empire in India (r. 270-232 B.C.E.). He converted to Buddhism and broadcast his precepts on inscribed stones and pillars, the earliest surviving Indian writing.
legalism
Chinese philosophy developed by Hanfeizi; taught that humans are naturally evil and therefore need to be ruled by harsh laws
Confucianism
Chinese ethical and philosophical teachings of Confucius which emphasized education, family, peace, and justice
ban Zhou
The first female Chinese historian who wrote about the Han dynasty in the first and second centuries CE.
Daoism
Chinese religion from 500s BCE that emphasized following the mystical and indescribable "Way." It celebrated the chaos and contradictions of reality as well as the harmony of nature. The Yin and Yang symbolizes many aspects of this religion.
Vedas
Ancient Sanskrit writings that are the earliest sacred texts of Hinduism.
Upanishads
A collection of over two hundred texts composed between 900 and 200 BC that provide philosophical commentary on the Vedas
Siddhartha Gautama
Founder of Buddhism
Theravada
'Way of the Elders' branch of Buddhism followed in Sri Lanka and much of Southeast Asia. It remains close to the original principles set forth by the Buddha; it downplays the importance of gods
Mahayana
"the Great Vehicle" - The largest of Buddhism's three divisions, prevalent in China, Japan and Korea, encompasses a variety of forms, including those that emphasize devotion and prayer to the Buddhas and bodhisattvas.
Bhagavad Gita
A book in popular Hinduism that was a response to Buddhism and made reaching moksha way easier.
The most important work of Indian sacred literature, a dialogue between the great warrior Arjuna and the god Krishna on duty and the fate of the spirit.
Zoroastrianism
One of the first monotheistic religions, particularly one with a wide following. It was central to the political and religious culture of ancient Persia.
A religion that developed in early Persia and stressed the fight between the forces of good and the forces of evil and how eventually the forces of good would prevail.
Judaism
A religion with a belief in one god. It originated with a covenant between God and Abraham and his descendants the Hebrew people. Yahweh was responsible for the world and everything within it. Holy Book is the Torah
Greek Rationalism
A secularizing system of scientific and philosophic thought that developed in classical Greece in the period 600 B.C.E. to 300 B.C.E.; it emphasized the power of education and human reason to understand the world in nonreligious terms.
Socrates
(470-399 BCE) An Athenian philosopher who thought that human beings could lead honest lives and that honor was far more important than wealth, fame, or other superficial attributes.
philosopher who believed in an absolute right or wrong; asked students pointed questions to make them use their reason, later became Socratic method. condemed to death for corrupting young minds.
Plato
Philosopher (429 BC-347 BC) who studied under Socrates and questioned reality. He believed that studying ideas and forms held the truth to what is real and wrote the Republic, which described an ideal state with philosopher-kings, warriors, and masses. He also creates the Academy, an ancient school of philosophy. "How do we know what is real" "Philosophy begins in wonder"
Aristotle
Greek philosopher. A pupil of Plato, the tutor of Alexander the Great, and the author of works on logic, metaphysics, ethics, natural sciences, politics, and poetics, he profoundly influenced Western thought. In his philosophical system, which led him to criticize what he saw as Plato's metaphysical excesses, theory follows empirical observation and logic, based on the syllogism, is the essential method of rational inquiry.
Jesus of Nazareth
Founder of Christianity, he taught about kindness and love for God. His teachings were based on Judaism and spread throughout the Roman Empire and the world.
Saint Paul
A man who is credited with the spread of Christianity throughout the roman empire. iIs letters that he wrote while under arrest by the Romans make up a large portion of the New testament.
Saint Peter
Early leader of the Christian church; one of Jesus's twelve apostles; also known as Simon Peter, the first pope of the Catholic Church
Church of the East
also known as the Nestorian Church,is a Christian church within of the Syriac tradition of Eastern Christianity. It was the Christian church of the Persian Sasanian Empire, and quickly spread widely through Asia. Between the 9th and 14th centuries it represented the world's largest Christian church in terms of geographical extent, with dioceses stretching from the Mediterranean to China and India. Several modern churches claim continuity with the historical Church of the East.
Perpetua
Woman from upper class Roman family who converted to Christianity was persecuted and died a martyr. Wrote a prison diary that describes her arrest and trial.
scholar gentry
Class that controlled much land and provided most candidates for civil service; replaced the old landed aristocracy as the political and economic elite of Chinese Dynasty; Agricultural society
Wang Mang
A Han court official who usurped the throne and ruled from 8 C.E. to 23 C.E.; noted for his reform movement that included the breakup of large estates.
Ge Hong
Born into an upper class family in China during troubled times (283-343 C.E.), his efforts to balance Confucian service to society and his own desire to pursue a more solitary and interior life in the Daoist tradition reflected the situation of many in his class
Yellow Turban Rebellion
A massive Chinese peasant uprising inspired by Daoist teachings that began in 184 C.E. with the goal of establishing a new golden age of equality and harmony.
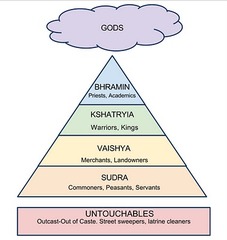
caste as varna and jati
distinct social class grouping; in China, Varna consisted of four classes that people were born into for life, and in India, Jati took on a similar form, but incorporated the specialized craftsman and guild workers into the system as well.
ritual purity in Indian social practice
In India, the idea that members of higher castes must adhere to strict regulations limiting or forbidding their contact with images and objects of lower castes to preserve their own caste standing and their relationship with the gods.
sutee/sati
This was a Hindu ritual that when your husband died you had to be burned alive next to him by force or volunteered
Greek and Roman slavery
In the Greek and Roman world, slaves were captives from war and abandoned children, and victims of Long-distance trade; manumission was common. Among the Greek household service was the most common form of slavery, but in parts of the Roman state, thousands of slaves were employed under brutal conditions in the mines and on great plantations
Spartacus
A Thracian sold to slavery to become a Gladiator. He led a revolt of slaves against the Rome forces and won. He hoped to escape to freedom but his army waged more wars, they planned to invade Sicily but were betrayed and defeated in 71 B.C. Six thousand of his men were crucified as a warning.
the "three obediences"
chinese women subject to father, then husband, then sons. confucianism.
Empress Wu
(690 - 705 C.E.) Tang ruler who supported Buddhist establishment; tried to elevate Buddhism to state religion; had multistory statues of Buddha created.
Aspasia and Pericles
Born to wealthy family, Aspasia was educated then moved to Athens where she met Pericles and they were a couple who treated each other equally. Pericles era as ruler is known as the 'Golden age of Athens'
Helots
In ancient Sparta, captive peoples who were forced to work for their conquerors
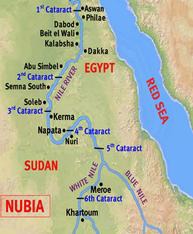
Meroë
Capital of a flourishing kingdom in southern Nubia from the fourth century b.c.e. to the fourth century c.e. In this period Nubian culture shows more independence from Egypt and the influence of sub-Saharan Africa.
Axum
The Christian state in Africa that developed its own branch of Christianity, Coptic Christianity, because it was cut off from other Christians due to a large Muslim presence in Africa.
Piye
king of Kush around 750 B.C., who gained control of Egypt, becoming pharaoh and uniting Egypt and Kush
Niger Valley Civilization
Distinctive city-based civilization that flourished from about 300 bce to about 900 ce; in the floodplain of the middle Niger and that included major cities like Jenne-jeno; the Niger valley civilization is particularly noteworthy for its apparent lack of centralize state structure, having veen organized in clusters of economically specialized settlements
Mayan civilization
a member of a major pre-Columbian civilization of the Yucatán Peninsula that reached its peak in the 9th century a.d. and produced magnificent ceremonial cities with pyramids, a sophisticated mathematical and calendar system, hieroglyphic writing, and fine sculpture, painting, and ceramics.