Volga River
The longest river in Europe and Russia's most important commercial river, includes canals connecting Moscow to the Baltic, Black, and Caspian Seas
Chinggis Khan
Born in 1170s in decades following death of Kabul Khan; elected khagan of all MOngol tribes in 1206; responsible for conquest of northern kingdoms of China, territories as far west as the Abbasid regions; died in 1227 prior to conquest of most of the Islamic world. Was shaministic, created a legal code and the Mongolian language to facilitate record keeping. 3 son problem at his death.
Muhammad Shah
The Turkic ruler of Khwarazm, __________ II, attempted to resist the Mongol conquest by Chingiss Khan but failed. Fled and left his people, he would later die on a island in the Caspian Sea.
Khwarazm
A old Islamic empire that was invaded by the mongols under Chingiss Khan.
Bukhara
City in Uzbekistan with an oasis on the Silk Road; former capital of Muslim dynasty(Khwarazm)
Caspian Sea
a large saltwater lake between Iran and Russia fed by the Volga River, the largest inland body of water; the largest lake made of salt water
Bamian
City where Chingiss Khans grandson died when they Mongols where attacking Muhammad Shah's Khwarazm. Was given the name "accursed city"
Karakorum
Capital of the Mongol empire under Chinggis Khan, 1162 - 1227.
Rashid al Din
Doctory, historian and adviser to the Il-khans, created some of the most concise writing on the Mongol Empire er who attempted the first history of the world
Khans
Mongol family that conquered a vast empire from Pacific to Danube River; there were five great these, the most famous was Kublai Khan of China.
Kabul Khan
Chinggis khan's great grandfather, defeats army of Jin Kingdom in northern China
Kuriltai
Meeting of all Mongol chieftans at which the supreme ruler of all Mongol tribes was selected.
Khagan
title of the supreme ruler of the Mongol tribes; Chinggis Khan chosen 1206
Tumens
Basic fighting units of the Mongol forces; consisted of 10,000 cavalrymen; each unit was further divided into units of 1000, 100, and 10.
Jebe
One of Chinggis' leading generals who first attracted his attention when he held his ground against overwhelming opposition and shot Chinggis' horse out from under him.
Tangut
Rulers of the Xi Xia kingdom of northwest china; one of the regional kingdoms during the period of Southern Song; conquered by Chinggis Khan's Mongols in 1226.
Jin Empire
A Chinese empire ormed by Jurchens (Manchurian people) attacked Song and the song empire eventually fell.Mongols 1211-Chinggis Khan attacked Jin.
Jurchens
Founders of Qin kingdom(Jin) that succeeded the Liao in northern China; annexed most of the Yellow River basin and forced the Song to flee south.
Kara Khitai Empire
An empire which had actually been established by Mongolian empire, Chinggis Khan mongols swiftly attacked it and annexed it.
Giovanni Carpini
The monk who asked the Mongols to join the Crusades(Pope Innocent the 4th sent him). He also wrote a book about the Mongolian empire.
Batu
Ruler of the golden horde; one of Chinggis Khan's grandsons; responsible for the invasion of Russia beginning in 1236.
Jochi
Eldest son of Genghis Khan and Borte. legitimacy was always questioned because of his conception time.
Ogedi
Third son of Chinggis Khan; succeeded Chinggis Khan as khagan of the Mongold following his father's death, Attacked Russia, E. Europe, Was a diplomat, not fighter,Islamic heartlands, and China
Golden Horde
One of four subdivisions of the Mongol Empire after Genghis Khan's Death; territory covered much of present south-central Russia, Mongol khanate founded by Genghis Khan's grandson Batu. It was based in southern Russia and quickly adopted both the Turkic language and Islam. Also known as the Kipchak Horde.
Khanates
Four regional Mongol kingdoms that arose following the death of Chinggis Khan.
Tatars
Mongols who captured Russian cities and destroyed the Kievan state in 1236. However, they left the Russian Orthodox church and aristocracy intact.
Alexander Nevskii
Prince of Novgorod. He submitted to the invading Mongols in 1240 and received recognition as the leader of the Russian princes under the Golden Horde.
Battle of Kulikova
Russian army victory over the forces of the Golden Horde; helped break Mongol hold over Russia
Prester John
In legends popular from the 12th to 17th centuries, he was a mythical Christian monarch whose kingdom was cut off from Europe by Muslim conquests; Chinggis Khan was originally believed to be this ruler.
Hulegu
Khubilai's brother who conquered the Abbasid dynasty and established the Ilkhanate of Persia. Captured the Abbasid capital of Baghdad after besieging it in 1258. Attempted to capture Syria but was expelled by Egyptian Muslims, who stopped Muslim expansion to the southwest, defeated Seljuk Turks.
Mamluks
Under the Islamic system of military slavery, Turkic military slaves who formed an important part of the armed forces of the Abbasid Caliphate of the ninth and tenth centuries. Mamluks eventually founded their own state, ruling Egypt and Syria , defeated MONGOLS.
Baibars
Commander of Mamluk forces at Ain Jalut in 1260; originally enslaved by Mongols and sold to Egyptians.
Ain Jalut
A battle when the Egyptians slaves stopped the Mongols from conquering all of the Muslim world
Berke
A ruler of the Golden Horde; converted to Islam; his threat to Hulegu combined with the growing power of Mamluks in Egypt forestalled further Mongol conquests in the Middle East.
Kublai Khan
Mongolian emperor of China and grandson of Genghis(chingiss) Khan who completed his grandfather's conquest of China and founded the Yuan dynasty
Yuan dynasty
Dynasty in China set up by the Mongols under the leadership of Kublai Khan, replaced the Song (1279-1368)
Dadu
In 1264, Khubilai established this new capital at the site of the Liao and Jin capitals. It became the main capital of the khanate of the Great Khan, which stretched from Mongolia through north China and Korea.
Chabi
Influential wife of Kubilai Khan; promoted interests of Buddhists in China; indicative of refusal of Mongol women to adopt restrictive social conventions of Chinese.
Marco Polo
Venetian merchant and traveler. His accounts of his travels to China offered Europeans a firsthand view of Asian lands and stimulated interest in Asian trade.,and he served Kublai Khan
The Romance of West Chamber
Chinese dramatic work written during the Yuan period; indicative of the continued literary vitality of China during Mongol rule.
White Lotus Society
Secret religious society dedicated to overthrow of Yuan dynasty in China; typical of peasant resistance to Mongol rule
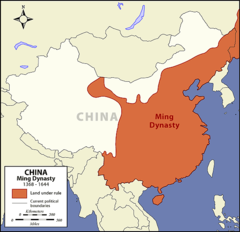
Ming Dynasty
A major dynasty that ruled China from the mid-fourteenth to the mid-seventeenth century. It was marked by a great expansion of Chinese commerce into East Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia, Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China.
Zhu Yuanzhang
A former monk that led this army in a final victory over the Mongols, became emperor of China and founded the Ming Dynasty
Timur-i-lang
Leader of Turkic nomads; beginning in 1360s from base at Samarkand, launched series of attacks in Persia, the Fertile Crescent, India, and southern Russia; empire disintegrated after his death in 1405
Ibn Khaldun
Arab historian. He developed an influential theory on the rise and fall of states. Born in Tunis, he spent his later years in Cairo as a teacher and judge. In 1400 he was sent to Damascus to negotiate the surrender of the city. Conversed with Tamerlane, proves the strangness of Tamerlane personality.
Black Death
An outbreak of bubonic plague that spread across Asia, North Africa, and Europe in the mid-fourteenth century, carrying off vast numbers of persons. Thought to be related to Mongolian Conquest and fleas on their horses/ equipment.