Bureau of Censors
Very powerful; their chief task was to keep track of officials at all levels and report their misdeeds or failings
Empress Wu
(690-750)
The only woman to rule China in her own name, expanded the empire and supported Buddhism during the Tang Dynasty.
*Elevated buddhism to status of state religion.
Empress Wei
Was married to the son of Empress Wu.
*She poisoned her husband.
She places her own small son as ruler, but this only lasted for 2 weeks because her attempt was thwarted by another prince. (he became Xuanzong 713-756)
Chan Buddhism
Chan variant of buddhism, also known as Zen in Japan and the west; stressed meditation and appreciation of natural and artistic beauty;
*popular with members of elite/educated Chinese in society
Pure Land Buddhism (MAHAYANA BUDDHISM)
Branch of Mahayana Buddhism that won widespread conversions because it provided a refuge from an age of war and turmoil.
Wuzong
841-847
Chinese emperor of Tang dynasty who openly persecuted Buddhism by destroying monasteries and shrines in 840s;
*hundreds of thousands of monks and nuns were forced to abandon their monastic orders and return to civilian lives.
-they and slaves who worked on their land were now subject to taxation of land.
-Monastery lands parceled out to taxpaying land lords and peasant small holders.
reduced influence of Chinese Buddhism in favor of Confucian ideology
Tea in China
Popular among the rich of China. In Hangzhou, Song people would have many pleasures of dining, listening, gambling and massages and sips of rice wine and tea.
Wendi
Member of prominent northern Chinese family during period of Six Dynasties;
-Struck a marriage alliance with daughter and ruler of Zhou empire.
-Seized son in law's position proclaimed himself emperor;
-Supported by nomadic peoples/nomad military commanders of northern China; (did this by refining desire to favor confucian scholar-gentry class)
-established Sui dynasty in early 589
Sui
Sui empire succeeded Han dynasty
Established in 589 by Wendi who rose to power by capturing son in law (zhou emperor's) throne.
-United all of Northern China and reconquered southern China.
Yangdi
Son of Wendi who murdered his father to reach the throne.
-Extended father's conquest and drove back nomadic intruders who threatened northern frontiers of empire.
-Established milder legal code and devoted resources to upgrading Confucian education.
-Sought to restore examination system for regulating entry into bureaucracy. **Promoted scholar gentry in the imperial administration. (This advancement was bad for aristocratic families and nomadic military commanders.)
Responsible for luxury and extravagant construction projects; palace @ Loyang; series of canals to link empire.
Led subjects into series of unsuccessful wars to bring Korea back to Chinese rule.
Assassinated in 618 by own ministers.
Footbinding
Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet in order to make them smaller; produced pain and restricted women's movement; made it easier to confine women to the household.
-Men preferred women with smaller feet.
Li Bo
most famous poet of the Tang era; blended images of the mundane world with philosophical musings.
Jin Kingdom
Kingdom north of the Song Empire.
Established by Jurchens, or nomadic contenders from the north, in 1115 after overthrowing Liao dynasty of the Khitans.
-Ended in 1234
Jurchens
Overthrew Liao dynasty of the Khitans and established the Jin kingdom in 1115. They were a new nomadic contender from the north.
Annexed most of Yellow river basin, causing the Song to flee to the south and establishing the QIN Empire.
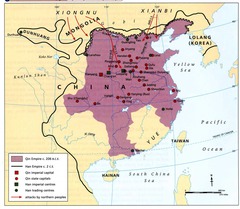
Qin Empire
A dynasty that replaced the Zhou dynasty in the 3rd century and the king used legalist ideas to unite his country.
They defeated invaders, doubled the size of china, murdered Confucius followers/burned books.
They built and improved water canals and irrigation and extended the great walls.
Champa Rice
Quick-maturing rice that can allow two harvests in one growing season. Originally introduced into Champa from India, it was later sent to China as a tribute gift by the Champa state (as part of the tributary system.)
Flying Money
Chinese credit instrument that provided vouchers to merchants to be redeemed at the end of a venture; reduced danger of robbery; an early form of currency.
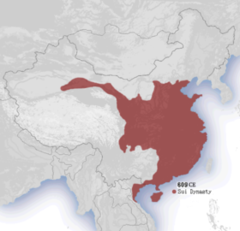
Changan
Capital of Tang dynasty; population of 2 million, larger than any other city in the world at that time.
Tangut Tribes
Rulers of Xi Xia kingdom of northwest China.
One of regional kingdoms during period of Southern Song
Was conquered by the Mongols in 1226
Xi Xia
Kingdom of the Tangut people, north of Song Kingdom, in the mid-11th century; collected tribute that drained Song resources and burdened chinese peasantry.
Jinshi
Title granted to students who passed the most difficult Chinese examination on all of Chinese literature; became immediate dignitaries and eligible for high office
Junks
Chinese ships equipped with watertight bulkheads, stern-post rudders, compasses, and bamboo fenders; dominant force in Asian seas east of the Malayan peninsula.
Gunpowder
The formula, brought to China in the 400s or 500s, was first used to make fumigators to keep away insect pests and evil spirits. In later centuries it was used to make explosives and grenades and to propel cannonballs, shot, and bullets.
Loyang
New capital of Sui, built by Yangdi
Neo-Confucians
Revived ancient Confucian teachings in Song era of China; great impact on the dynasties that followed; their emphasis on tradition and hostility to foreign systems made Chinese rulers and bureaucrats less receptive to outside ideas and influences.
Sinification
Extensive adaptation of Chinese culture in other regions; typical of Korea and Japan, less typical of Vietnam.
Ministry of Public Rites
Administered the examinations for state office during the Tang dynasty.
Huangzhou
Capital of the Southern SONG; location near East China Sea which permitted international commerce; population of more than 1,500,000. Capital of the Northern Song was Kaifeng.
Liao Dynasty
Founded in 907 by nomadic Khitan peoples from Manchuria; maintained independence from Song dynasty in China.
Chen kingdom
Kingdom to the south of Sui China that was conquered through the help of the later Zhou dynasty
Southern Song
Smaller surviving dynasty (1127-1279); presided over one of the greatest cultural reigns in world history.
Li Yuan, Duke of Tang
Duke of Tang who was a minister for for Yangdi. Took over the empire after Yangdi's assassination and was the first Tang ruler.
Kaozong
Emperor who in 668 sent armies to take over Korea, created a vassal kingdom called Silla
Tang Taizong
(627- 649) Son of Li Yuan. He reconquered the northern and western land that China had since the decline of the Han Dynasty. He started the achievements of the Tang Dynasty.
Xuanzong
Emperor from 712-756 ,This emperor marked the peak of Tang power, Took strong interest to political and economic reforms and turned to pleasures and arts. Fell in love with Yang Guifei after death of second wife and started ignoring the Tang to keep her happy
An Lushan
one of Yang Guifei's proteges, that launched a rebellion in 755 and briefly seized the capitol of Chang'an. When the rebellion was stopped, Yang Guifei was put to death.
Foreign-born general who led a major revolt against the Tang dynasty in 755-763, perhaps provoking China's turn to xenophobia
Zhu Xi
(1130-1200) Most prominent of neo-Confucian scholars during the Song dynasty in China; stressed importance of applying philosophical principles to everyday life and action
Liao
Northern Song's less wealthy, yet much more powerful neighbors whom the Song would pay to keep them from invading
Taizu
960 1st emperor to reunite China; made Song Dynasty; never regained W & N lands (paid tribute to N)
Zhao Kuangyin
Founder of Song dynasty; originally a general following fall of Tang; took title of Taizu; failed to overcome northern Liao dynasty that remained independent.
Yang Guifei
Royal concubine of Tang emperor Xuanzong; introduction of relatives into administration led to revolt.
Wang Anshi
Confucian scholar and chief minister of a Song emperor in 1070s; introduced sweeping reforms based on Legalists; advocated greater state intervention in society.
Subprefecture
The district level of the Chinese bureacracy, similar to an American county