Second Industrial Revolution Characteristics
- steel, chemicals, electricity and petroleum led the way
- new products -- steel machinery;
- electricity for energy and light;
- internal combustion engine brought new power for transportation
- industrial production grew at a rapid rate
- industrial core - Great Britain, Belgium, France, Netherlands, Germancy part of Austro-Hungary, northern Italy
- higher standard of living
Gugliemo Marconi
He was a pioneer of radio waves. He built the first radio.
Thomas Edison
Inventor of the light bulb
Internal Combustion Engine
This machine created a major shift in the transportation of goods and people. It was powered by oil and gasoline.
Orville & Wilbur Wright
designed and flew the first airplane at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina
Karl Marx
developed socialism in response to the evils of Industrial Revolution and wrote the Communist Manifesto
The Communist Manifesto
Pamphlet written by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels and became the basis of Socialism.
Revisionists
a Marxist who rejected the revolutionary approach, believing instead in evolution by democratic means to achieve the goal of socialism
Bourgeoisie
the middle class, including merchants, industrialists, and professional people
Proletariat
the working class
Ministerial Responsibility
the idea that the prime minister is responsible to the popularly elected executive body and not to the executive officer
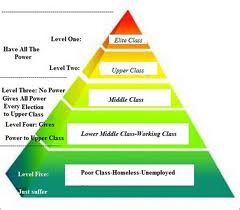
The New Elite
a very small group (5%) that controlled a large percent of the wealth (30%-40%). They were landed aristocrats, industrialists, bankers and merchants who were the leaders in government and the military.
Rural vs. Urban Populationi Growth
Urban populations grew through vast migration from rural areas
- urban areas offered jobs, improved housing and running water
- rural populations flocked to cities because of lack of land and lack of jobs
Emmeline Pankhurst
a feminist of woman's rights and founder of the Woman's Social and Political Union .
Women's Social & Political Union
Established in 1903 by Emmeline Pankhurst. Used unusual publicity stunts to call attention to their demands. They had one basic aim which was the right of woman to full citizenship in the nation state.
Amalie Sieveking
a nursing pioneer who founded the Female Association for the Care of the Poor and Sick in Hamburg.
Trade Unions
early labor organizations that brought together workers in the same trade or job to fight for better wages and working conditions
Czar Nicholas II and the Duma
A Russian ruler who believed in absolute power. In 1905 workers tried to present a petition of complaints to the Czar and his troops opened fire on them killing hundreds. Nicholas II was latered forced to grant civil liberties and created a legislative assembly, called the Duma.
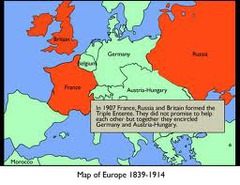
Triple Entente
Alliance between Russia, France, Great Britain who stood opposed to the Triple Alliance (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy).
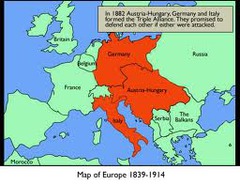
Triple Alliance
1882 - united the powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy in a defensive alliance against France.
Marie Curie
French scientist who worked with radioactive materials and discovered radium.
Albert Einstein
German-born scientist provided a new view of the universe. Published special theory of relativity. Space and time depend on human experience.
Social Darwinism
Applied Darwin's theory of natural selection and "survival of the fittest" to human society -- the poor are poor because they are not as fit to survive. Used as an argument against social reforms to help the poor.
Impressionism
A movement in 19th century painting, in which artists reacted against realism by seeking to convey their impressions of subjects or moments in time. These artists wanted to show the effect of light on objects or scenes they painted and using scences of everyday life indoors and outdoors.
Symbolists
a group of writers that caused a literary revolution.
Post-Impressionism
the French art movement that immediately followed Impressionism
Pablo Picasso
a Spanish artist, founder of Cubism, which focused on geometric shapes and overlapping planes
Claude Monet
Impressionist painter who used color rather than shape to show emphasis; Painted a subject several times in different lights (Rouen Cathedral); Water Lilies, Japanese Bridge
Vincent Van Gogh
Dutch postimpressionist painter noted for his use of color (1853-1890)
Functionalism
A new principle of building design that focused on buildings being functional which means serving the purpose it was made for best
Sigmund Freud
A docor from Vienna who proposed a series of theories that raisedquestions about the nature of the human mind.