Eli Whitney
inventor of the cotton gin and interchangeable parts
Mass Production
the making of goods in large quantities made possible by factories, machinery and the division of labor
Henry Clay
Speaker of the House of Representatives from Kentucky who promoted the American System
American System
an economic regime pioneered by Henry Clay which created a high tariff to support internal improvements such as road-building. This approach was intended to allow the United States to grow and prosper by themselves. This would eventually help America industrialize and become an economic power.
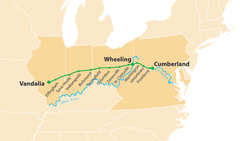
National Road
First national road building project funded by Congress. It made travel and transportation of goods much easier because it was one continuous road that was in good condition.
Monroe Doctrine
an American foreign policy opposing interference in the Western hemisphere from outside powers
Tariff of 1816
a protective tariff designed to aid American industries
Mc Culloch v Maryland
Supreme court case that denied Maryland the right to to tax the bank of the US
John Quincy Adams
6th President of the United States
Nationalism
belief that national interests are more important than regional differences
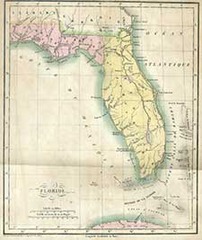
Adams-Onis Treaty
Treaty that secured Florida from Spain
Missouri Compromise
The issue was that Missouri wanted to join the Union as a slave state, therefore unbalancing the Union so there would be more slave states then free states. The compromise set it up so that Maine joined as a free state and Missouri joined as a slave state. Congress also made a line across the southern border of Missouri saying except for the state of Missouri, all states north of that line must be free states or states without slavery.
Andrew Jackson
The seventh President of the United States (1829-1837), who as a general in the War of 1812 defeated the British at New Orleans (1815). As president he opposed the Bank of America, objected to the right of individual states to nullify disagreeable federal laws, and increased the presidential powers.
Democratic-Republican Party
Party started by Jackson Followers that wanted a weak central government
Spoils System
system in which incoming political parties throw out former government workers and replace them with their own friends
Indian Removal Act
passed in 1830 by Congress; it called for the government to negotiate treaties that would require the Native Americans to relocate West.
Trail of Tears
an 800 mile forced march made by the Cherokee from their homeland in Georgia to Indian Territory; resulted in the deaths of thousands of Cherokee
John C. Calhoun
South Carolina Senator - advocate for state's rights, limited government, and nullification
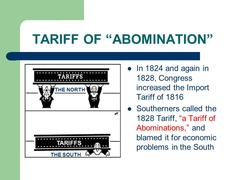
Tariff of Abominations
Henry Clay's name for an 1828 tariff increase
Daniel Webster
Senate leader from Massachussetts who defended federal powers. He opposed Calhoun and debated Robert Hayne
Martin Van Buren
8th President of the United States (1782-1862)
Bank of the United States
National bank established by congress
Whig Party
An American political party formed in the 1830s to oppose President Andrew Jackson and the Democrats, stood for protective tariffs, national banking, and federal aid for internal improvements
Panic of 1837
a series of financial failures that led to an economic depression
William Henry Harrison
9th President of the United States
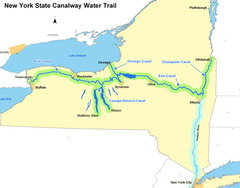
Erie Canal
"Big Ditch", canal that connected the Great Lakes with the Atlantic Ocean making New York a dominant port
Election of 1824
"corrupt bargain"- Adams became the president when Clay gave his support for Adams in exchange for naming Clay Secretary of State
corrupt bargain
Refers to the presidential election of 1824 in which Henry Clay, the Speaker of the House, convinced the House of Representatives to elect Adams rather than Jackson.
2nd Great Awakening
a 19th century religious movement in which individual responsibility for seeking salvation was emphasized, along with the need for personal and social improvement
revival
religious gathering designed to reawaken faith
Ralph Waldo Emerson
American transcendentalist who was against slavery and stressed self-reliance, optimism, self-improvement, self-confidence, and freedom. He was a prime example of a transcendentalist and helped further the movement.
Charles Finney
Preacher who held the first of many religious revivals
Transcendentalism
A philosophy stressing the relationship between human beings and nature, spiritual things over material things and the importance of the individual conscience