culture
a shared set of meanings that are lived through the material and symbolic practices of everyday life.
cultural geography
focuses on the way in which space, place, and landscape shape culture at the same time that culture shapes space, place, and landscape.
folk culture
traditional practices of small groups, especially rural people with a simple lifestyle (compared with modern, urban people), such as the Amish in Pennsylvania or the Gypsies in Europe, who are seen to be homogeneous in their belief systems and practices.
popular culture
the practices and meaning systems produced by large groups of people whose norms and tastes are often heterogeneous and change frequently, often in response to commercial products.
cultural landscape
a characteristic and tangible outcome of the complex interactions btw a human group- with its own practices, preferences, values, and aspirations-and its natural environment.
historical geography
the geography of the past.
Genre de vie
a key concept in Vidal de la Blache's approach to cultural geography in France, referred to a functioning organized way of life that was seen to be characteristic of a particular culture group. centered on the livelihood practices of a group that were seen to shape physical, social, and psychological bonds.
cultural trait
a single aspect of the complex of routine practices that constitute a particular cultural group.
dietary law for Muslims prohibits the consumption of pork.
rites of passage
ceremonial acts, customs, practices, or procedures that recognize key transitions in human life- birth, menstruation, and other markers of adulthood such as sexual awakening and marriage.
cultural complex
the combination of traits characteristic of a particular group.
Avoidance of pork, the celebration of bar/bat mitzvah, constitute the cultural complex of Judaism.
cultural region
an area where certain cultural practices, beliefs, or values are more or less practiced by the majority of the inhabitants.
Utah is considered to be a Mormon cultural region.
cultural system
includes traits, territorial affiliation, and shared history as well as other, more complex elements, such as language.
Christianity unites all protestant religions, yet the practices of particular denominations vary.
religion
a belief system and a set of practices that recognizes the existence of a power higher than humans.
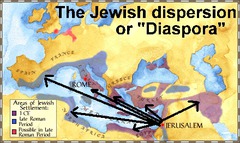
diaspora
a spatial dispersion of a previously homogeneous group.
language
a means of communicating ideas or feelings by means of a conventionalized system of signs, gestures, marks, or articulate vocal sounds.
dialects
regional variations in standard languages
language family
a collection of individual languages believed to be related in their prehistorical origin.
language branch
a collection of languages that possess a definite common origin but have split into individual languages.
language group
a collection of several individual languages that are part of a language branch, that share a common origin in the recent past, and have relatively similar grammar and vocabulary.
spanish, french, portuguese, italian, romanian, and catalan are a language group, classified under the romance branch as part of the indo-european language family.
cultural hearths
the geographic origins or sources of innovations, ideas or ideologies.
kinship
normally thought of as a relationship based on blood, marriage, or adoption.
tribe
a form of social identity created by groups who share a set of ideas about collective loyalty and political action.
cultural nationalism
a effort to protect regional and national cultures from the homogenizing impact of globalization, especially from the penetrating influence of U.S. culture.
Islam
a Arabic term that mean's "submission," specifically submission to God's will.
Muslim
a member of the community of believers whose duty is obedience and submission to the will of God.
hajj
making at least one pilgrimage to Mecca if financially and physically able.
Islamism
an anticolonial, anti-imperial, and generally anticore political movement. resist modernization and secularization. not all muslims are islamists, although Islamism is the most militant movement w/in Islam today.
jihad
a sacred struggle. when this struggle is violently directed against the enemies of Islam, jihad is understood to be a holy war. but jihad can also be a sacred struggle to establish Islam as a universal religion through the conversation of nonbelievers.
struggle of Shi'ite Muslims for social, political, and economic rights w/in Sunni-dominated Islamic states.
sexuality
a set of practices and idendities that a given culture considers related to each other and to those things it considers sexual acts and desires.
ethnicity
a socially created system of rules about who belongs to a particular group based upon actual or perceived commonalities, such as language or religion.
race
a problematic classification of human beings based on skin color and other physical characteristics.
racialization
the practice of creating unequal castes where whiteness is considered the norm or unexceptional.
gender
a category reflecting the social differences btw men and women.
world music
the musical genre defined largely in response to the sudden increase of non-English language recordings released in the UK and the US in the 1980s.