Nevirapine
Viramune) is a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor that is used to treat HIV infection. It is used in combination with other antiretroviral medications to treat HIV. Adverse effects include rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, hepatitis, and increased transaminase levels.
zidovudine
Retrovir)
AZT, ZDV
to treat AIDS by blocking the growth of AIDS and to prevent pregnant women with HIV from passing the virus to their babies
A common side/adverse effect is leukopenia and anemia.
monitor the complete blood count results for changes.
Didanosine
Videx) can cause pancreatitis. A serum amylase level that is increased 1.5 to 2 times normal may signify pancreatitis in the client with AIDS and is potentially fatal. May have to D/C the med. hepatotoxic and can result in liver failure.
HIV->drug->pancreatitis
cyclosporine
Sandimmune), complaining of a headache, the blood pressure is to be monitoring most closely. adverse effects include infection, nephrotoxicity, and hirsutism
order postoperatively for a transplant
Immunosuppressant
grapefruit juice can raise cyclosporine levels by 50% to 100%, .
aminoglycoside
-cin
Gentamycin, Kanamycin sulfate, Neomycin sulate, Steptomycin Sulfate
ototoxic and nephrotoxic, confusion, disorientation GI irritation, vertigo
Ringing in the ears and vertigo are two symptoms that may indicate dysfunction of cranial nerve VIII.
Amikacin
Amikin
aminoglycoside.
ototoxicity , confusion, GI problems, palpitations, BP changes, nephrotoxicity, and hypersensitivity. instructs the client to report hearing loss to the HCP immediately.
hearing acuity tests and kidney function studies should be performed before the initiation of therapy
Foscarnet
toxic to the kidneys. Serum creatinine is monitored before therapy, 2 -3 /week during induction therapy and weekly during maintenance therapy. cause decreased levels of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium. these levels are also measured with the same frequency.
pentamidine isethionate
(Pentam 300
Frequent side/adverse effects of this medication include leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia. The client should be monitored routinely for signs and symptoms of infection.
used to prevent opportunistic pneumonia with AIDS patients; effective if decrease in crackles and dyspnea

Saquinavir
Invirase) is an antiretroviral (protease inhibitor) used with other antiretroviral medications to manage human immunodeficiency virus infection. Saquinavir is administered with meals and is best absorbed if the client consumes high-calorie, high-fat meals. Saquinavir can cause photosensitivity, and the nurse should instruct the client to avoid sun exposure.
Protease inhibitor
Fortovase, Invirase
bioavailability ^ with high fat food
. It is administered within 2 hours after a full meal. If the medication is taken without food in the stomach, it may result in no antiviral activity
Ketoconazole
is an antifungal medication. It is administered with food (not on an empty stomach), and antacids are avoided for 2 hours after taking the medication to ensure absorption. The medication is hepatotoxic, and the nurse monitors liver function studies. The client is instructed to avoid exposure to the sun because the medication increases photosensitivity. The client is also instructed to avoid alcohol.
Nizoral
Elevated liver enzymes
Stavudine
d4t, Zerit) is an antiretroviral used to manage human immunodeficiency virus infection in clients who do not respond to or who cannot tolerate conventional therapy. The medication can cause peripheral neuropathy, and the nurse should monitor the client's gait closely and ask the client about paresthesia.
Fexofenadine
is an antihistamine, which provides relief of symptoms caused by allergy. Antihistamines should be discontinued for at least 3 days (72 hours) before allergy skin testing to avoid false-negative readings. This client should have the appointment rescheduled for 3 days after discontinuing the medication.
(Allegra
Mycophenolate mofetil
should be administered on an empty stomach. The capsules should not be opened or crushed. The client should contact the HCP if unusual bleeding or bruising, sore throat, mouth sores, abdominal pain, or fever occurs because these are adverse effects of the medication. Antacids containing magnesium and aluminum may decrease the absorption
Immunosuppressant
tacrolimus (Prograf
Imminosuppressant
organ transplants
A blood glucose level is elevated above the normal range of 70 to 110 mg/dL and suggests an adverse effect. Other adverse effects include neurotoxicity evidenced by headache; tremor; insomnia; gastrointestinal (GI) effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting; hypertension; and hyperkalemia.
used concurrently with adrenal corticosteroids
Lamivudine
Epivir
Reverse transcriptase inhibitor
HIV, hepatitis
is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor and antiviral medication. It slows HIV replication and reduces the progression of HIV infection. It also is used to treat chronic hepatitis B and is used for prophylaxis in health care workers at risk of acquiring HIV after occupational exposure
Cyclosporine is an immunosuppressant medication. Because of the medication's effects, the client should not
receive any vaccinations without first consulting the HCP. The client should report decreased urine output or cloudy urine, which could indicate kidney rejection or infection, respectively. The client must be able to self-monitor blood pressure to check for the side effect of hypertension. The client needs meticulous oral care and dental cleaning every 3 months to help prevent gingival hyperplasia.
Azathioprine
Azasan, Imuran
FOR: organ transplantation, RA, Crohn's, SL
Causes bone marrow suppression
is an immunosuppressant medication that is taken for life. Because of the effects of the medication, the client must watch for signs of infection, which are reported immediately to the HCP. The client should also call the HCP if more than one dose is missed. The medication may be taken with meals to minimize nausea.
MMR vaccine
measles, mumps, rubella
is administered subcutaneously in the outer aspect of the upper arm.
Administered 12-15months of age and repeated at 4-6 years or by 11-12 years of age; contraindicated for persons with hx of anaphylactic reaction to neomycin or eggs, those with known altered immunodeficiency, and pregnant women; SC at different sites, may have a light transient rash for 2 weeks after administration of vaccine
kidney
Nephr/o
Ren/o
nephrotoxic
damage to the kidneys by a toxic substance
preexisting hearing loss is a contraindication for
the administration of aminoglycosides because these medications can cause ototoxicity and irreversible hearing loss. The nurse should report the findings to the RN to protect the client's safety. The RN will in turn notify the health care provider.
Amoxicillin
is a type of penicillin. Frequent side effects include mild gastrointestinal disturbances, headache, and oral or vaginal candidiasis-vaginal drainage
contraindication to receiving the hepatitis B vaccine
is a previous anaphylactic reaction to common baker's yeast.
Nelfinavir
is an antiviral medication used in the treatment of HIV infection when antiretroviral therapy is warranted. It is available in tablet and powder form. The powder form is prepared by mixing the dose with a small amount of water, milk, formula, soy milk, or dietary supplements. The powder is not mixed with acidic foods or juices
PI
Protease Inhibitor
Viracept
Worst PI for diarrhea
Zidovudine
Retrovir
AZT
Which drug is used to prevent pregnant women with HIV from passing the virus to their babies?
interferes with HIV replication, slowing the progression of HIV infection. The client is instructed to space the doses of the medication evenly around the clock. Food or milk does not affect the gastrointestinal absorption of the medication. The client is instructed to continue therapy for the full length of treatment.
Peripheral neuropathy,
characterized by numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands or feet,
Ritonavir oral solution
is preferably administered with a food substance. It may be mixed with chocolate milk or a dietary supplement to improve the taste. The client also is instructed to consume the dose within 1 hour of mixing.
IVIG
intravenous immune globulin
meds. decreasing the immune rsponse by being 'bait' for the body to attack.
is an immune serum that increases antibody titer and antigen-antibody reaction, providing passive immunity against infection. Anaphylactic reactions, although rare, can occur, and the nurse ensures that epinephrine is readily available when administering this medication.
Protamine sulfate
is the antidote for heparin.

Vitamin K
Phytonadione,Phylloquinone
Antidote for Coumadin, Wararin
Efavirenz (Sustiva
antiRETROviral (NNRTI)
Because the medication causes temporary nervous system side effects during the first 2 to 4 weeks of therapy, the client is instructed to take the medication at bedtime. Because of the nervous system effects,
Indinavir
is an antiretroviral agent. This medication can cause kidney stones; therefore, the client is instructed to increase fluid intake to at least 1.5 L/day. The client is also instructed to report sharp back pain or the presence of blood in the urine. The client is instructed to take the medication 1 hour before or 2 hours after a large meal. If the medication needs to be taken with food, the client should consume a light meal, such as dry toast, juice, or a bowl of cereal with milk
Lamivudine
is an antiretroviral agent administered in combination with zidovudine to delay the appearance of zidovudine resistance. Lamivudine is well absorbed orally with or without food. Peripheral neuropathy can occur with its use, and the client is instructed to notify the health care provider if burning, numbness, or tingling of the hands, arms, feet, or legs occurs. Pancreatitis, evidenced by nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, is also an adverse effect of the medication
Moxifloxacin
is a fluoroquinolone. Increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight can occur, and the client is instructed to avoid excessive sunlight and artificial ultraviolet light. The client should wear sunscreen and protective clothing when outdoors. The client should also drink fluids liberally and avoid the use of antacids

fluoroquinolone
causes tendonitis, tendon rupture, tooth damage, cartilage damage
-Ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, levofloxacin, ofloxacin, moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin, enoxacin
client with TB who is coinfected with HIV
requires that antitubercular therapy last longer than usual. The prescription is usually for a total of 9 months and at least 6 months after sputum cultures convert to negative.
Ganciclovir
Antiviral
causes neutropenia and thrombocytopenia as the most frequent side effects. For this reason, the nurse monitors the client for signs and symptoms of bleeding and implements the same precautions that are used for a client receiving anticoagulant therapy. Thus, the client should be instructed to use an electric rather than a straight razor for shaving
thrombocytopenia
deficiency of clotting cells
low platelet count
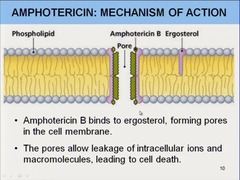
Amphotericin B
Antifungal
anti-fungal. HIGHLY Toxic
is a toxic medication that can produce symptoms during administration such as chills, fever, headache, vomiting, and impaired renal function-check output of urine
. The medication is also very irritating to the IV site, commonly causing thrombophlebitis. The nurse administering this medication watches for all of these problems.
amphotericin B may develop nephrotoxicity. Clients should be monitored for oliguria, hematuria, cloudy urine, decreased urine output, and elevated renal function laboratory values.
tetracycline hydrochloride
can cause staining of the teeth, straws should be used, and the mouth should be rinsed
causes photosensitivity and increased severity of sunburn
Contraindicated in pregnancy an lactation. .
No milk, calcium, or antacids within an hour of tetracycline. / Effective against gonorrhea, syphilis, and chlamydial infections
Metronidazole
Flagyl
DOC for giardia, bacterial vaginosis, pseudomembranous colitis, and trichomonas
Harmless darkening of the urine may occur, and the client should be forewarned of this effect.
acyclovir (Zovirax
Antiviral
Genital herpes herpes simple anti viral
most common reaction related to the administration of this medication is phlebitis and inflammation at the intravenous site of infusion. Reversible nephrotoxicity manifested as elevations in serum creatinine and
blood urea nitrogen also occur
Ribavirin
is active against RSV, influenza virus types A and B, and herpes simplex virus. It is administered by inhalation, and the
medication is absorbed from the lungs and achieves high concentrations in respiratory tract secretions and erythrocytes. It is not administered orally, subcutaneously, or intramuscularly.
RSV
respiratory syncytial virus
Name the most common cause. • Hospitalization in children younger than 1 year of age
Contact
Tacrolimus
is an immunosuppressant medication used in the prophylaxis of organ rejection in clients receiving allogenic liver transplants. It should be used concurrently with adrenal corticosteroids. It may also be used in clients receiving kidney, bone marrow, heart, pancreas, and small bowel transplants
allogenic
other donor but properly screened
Rifampin (Rifadin
The client needs to avoid alcohol while taking this medication. The medication should be taken on an empty stomach with 8 ounces of water 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals. The client should be told that urine, feces, sweat, and tears may turn red-orange. The client should also be instructed that doses should not be skipped and that the medication needs to be taken as prescribed for the full length of therapy, which may range from 6 to 9 months up to 1 year. The nurse should note any elevation of the alkaline phosphatase, which would indicate possible hepatotoxicity.
client may be on the medication for 12 months even if cultures are negative.
wear glasses instead of contacts because they may be permanently damaged by the orange discoloration that rifampin causes in body fluids
Oseltamivir
is an oral antiviral medication used to treat influenza A and B virus
Tamiflu
Antiviral
Nitrofurantoin sodium
is an antibacterial agent and is used to treat acute urinary tract infection or as chronic suppressive treatment of urinary tract infection. It is not effective with systemic bacterial infections. Because dysuria is a sign of a urinary tract infection,
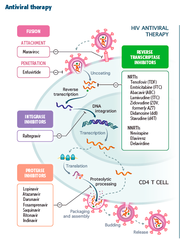
zidovudine
include headache, malaise, insomnia, rash, diarrhea, and fever. As AZT therapy proceeds, these symptoms become more tolerable. If anemia or neutropenia occurs, the medication will be discontinued or the therapy will be temporarily interrupted
AZT
AZT, ZDV
Which antiretroviral is most likely to cause anemia?
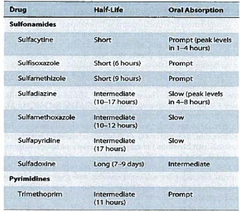
Sulfisoxazole
is an anti-infective used primarily to treat urinary tract infections. The effectiveness of the medication may be evaluated by monitoring the client's white blood cell count, which should decrease to within normal limits with therapy. The client should also experience relief of symptoms.
Sulfonamide
What sulfonamide is the drug of choice in treating: UTIs?
Aerosolized pentamidine
is given prophylactically to clients with a T4 count below 200 to prevent Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, which is the most common opportunistic infection that occurs in clients with AIDS. A respiratory rate and depth within normal limits for activity level would indicate that the client was not experiencing the respiratory difficulty that is associated with pneumonia.
Inhaled, can prevent occurence of PCP
Itraconazole
Sporanox
antifungal
is an antifungal medication. The client should be instructed to take the medication with food because it increases the absorption of the medication. Fluids should be increased to prevent constipation, which can occur as a side effect. Hepatitis is an adverse reaction associated with the medication, and if the client develops any anorexia, abdominal pain, unusual tiredness or weakness, dark urine, or jaundice, the health care provider should be notified.
kanamycin sulfate
Kantrex
Kantrim, Kantrex
include nephrotoxicity evidenced by an increased BUN and creatinine and decreased creatinine clearance. Irreversible ototoxicity as evidenced by tinnitus, dizziness, ringing in the ears, and reduced hearing, and neurotoxicity as evidenced by headache, dizziness, lethargy, and visual disturbances can occur. Gastrointestinal disturbances can occur as a frequent side effect of the medication. An elevated white blood cell count may occur as a result of the respiratory infection.
Metronidazole
Flagyl
Antibacterial/Antiprotozoal
can produce a variety of untoward effects, but they rarely require termination of treatment. Harmless darkening of the urine may occur, and the client should be told of this effect. It is not necessary to discontinue the medication or call the health care provider. Increasing fluid intake is a good health measure but will not prevent this side effect from occurring.
indinavir (Crixivan
The medication should be stored at room temperature and protected from moisture because moisture can degrade the medication and affect its potency.
antiRETROviral (Protease inhibitor)
erythromycin
Macrolid
In patients who are allergic to penicillin, what is the most appropriate antibiotic alternative?
should be administered on an empty stomach with a full glass of water.
Pentamidine isethionate
- NebuPent
Pentam 300, Nebupent
causes severe hypoglycemia that may be fatal. Other toxic effects include hypotension, dysrhythmias, leukopenia, nephrotoxicity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, hyperglycemia, and type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Amoxicillin is a penicillin. Adverse reactions
include superinfections such as potentially fatal antibiotic-associated colitis, which results from altered bacterial balance. Symptoms include abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, and fever.
ceftriaxone
Cervical gonorrhea is treated with one (125 mg) inject or . Allergies to penicillin may contraindicate giving ceftriaxone, and slight discomfort at the injection site is common.
Rocephin
Gonorrhea prophylaxis
cefixime
Suprax)
one (400 mg) oral dose of
oral administration
Infliximab
is a monoclonal antibody and gastrointestinal anti-inflammatory. Allergic reactions and anaphylaxis can occur from this medication and can be fatal. This complaint could be the first sign of an anaphylactic reaction. The RN must be notified, and it is imperative that the infusion be shut off as soon as possible. Then the health care provider must be notified.
Remicade
Immunosuppresson
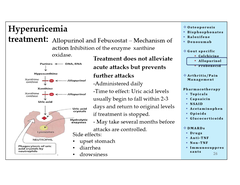
Allopurinol
is an antigout medication that may increase the effect of oral anticoagulants. Warfarin sodium is an anticoagulant, and if this medication was prescribed for the client, the nurse should verify the prescription.
The dose of warfarin sodium may need to be decreased.
Aloprim, Zyloprim
Push fluids
warfarin
Coumadin
Anticoagulant
A nurse is obtaining the medication history of a client who is starting a new prescription for allopurinol.
Which of the following medications should the nurse contact the provider regarding a potential interaction?
Varicella vaccine
is recommended at any visit at or after age 12 months for susceptible children
Methenamine
is contraindicated in clients with renal or hepatic disease or those with severe dehydration. The nurse would question the health care provider's prescription for this medication in the client with cirrhosis.
Hiprex
Frequency of urinary tract infections decreases.
Nalidixic acid
can intensify the effects of oral anticoagulants. When an oral anticoagulant is combined with nalidixic acid, a reduction in the anticoagulant dosage may be needed.
For UTI caused by Proteus
fluoroquinolone
prograf
Tacrolimus is used with caution in immunosuppressed clients and those with renal or hepatic function impairment.
Tacrolimus (systemic)
Organ rejection prophylaxis
nitrofurantoin,
the urine pH must be maintained in an acid range. The client should consume an acid-ash diet. Rhubarb will reduce the acidity of the urine and should be avoided by the client taking this medication.
Macrobid, Macrodantin, Furadantin
Used for recurrent UTI
Antibiotic
Saquinavir
is an antiviral medication. It is administered within 2 hours after a full meal. If the medication is taken without food in the stomach, it may result in no antiviral activity.
Protease inhibitor
Invirase
Ganciclovir
Cytovene
SE: neutropenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
causes neutropenia and thrombocytopenia as the most frequent side effects. For this reason, the nurse monitors the client for signs and symptoms of bleeding and implements the same precautions that are used for a client receiving anticoagulant therapy. Thus, the client should be instructed to use an electric rather than a straight razor for shaving.
trimethoprim
(Proloprim
is a sulfonamide used to treat urinary tract infections. Each dose of trimethoprim should be taken with a full glass of water, and the client should maintain a high fluid intake. The client should not be instructed to discontinue the medication. Some forms of sulfonamides cause the urine to turn dark brown or red. This is an expected effect,
Nelfinavir
is an antiviral medication used in the treatment of HIV infection when antiretroviral therapy is warranted. It is available in tablet and powder form. The powder form is prepared by mixing the dose with a small amount of water, milk, formula, soy milk, or dietary supplements. The powder is not mixed with acidic foods or juices
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
is a sulfonamide. The client takes each dose with 8 oz of water and drinks several extra glasses of water each day. The client should space doses evenly around the clock for stable blood levels and should take medication for the full course of therapy. The client should report rashes or other skin changes, which could indicate an allergy to sulfa.
Cyclosporine
is an immunosuppressant. To avoid toxicity from high drug levels and to avoid organ rejection from low drug levels, blood levels of cyclosporine should be measured periodically. In the organ transplant client, an immunosuppressant will need to be taken for life. Oral administration is the route of choice; intravenous administration is reserved for clients who cannot take the medication orally. The most serious adverse effects are nephrotoxicity and infection.

Vancomycin
Drug used for MRSA
is classified as a tricyclic glycopeptide antibiotic and acts by producing a bactericidal effect. Therapeutic serum levels are drawn on a regular basis to ensure effectiveness of this medication. The nurse should monitor hearing acuity, kidney function studies, and heart rate and blood pressure because this medication can be ototoxic, nephrotoxic, and cardiotoxic;
serum potassium level
should be 3.5 mEq/L or higher
Thiazide diuretics
such as hydrochlorothiazide are sulfa-based medications, and a client with a sulfa allergy is at risk for an allergic reaction. A sulfa allergy must be communicated to the pharmacist,
Dapsone
may be prescribed for the treatment of toxoplasmosis. The medication is taken orally on a daily basis. The medication suppresses bone marrow activity, and the complete blood count is monitored closely. If the client develops fever, sore throat, purpura, or jaundice, the HCP is notified because this could indicate infection.
Sulfur drug
toxoplasmosis
What is the most common opportunistic infection of the CNS in HIV?
Ring-enhancing brain lesion in HIV patient
What is spread by oocysts in cat feces
