Paleolithic
The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans. and also when people made tools from stones, and were hunters.
Neolithic
(10,000 - 8,000 BCE) The development of agriculture and the domestication of animals as a food source. This led to the development of permanent settlements and the start of civilization.
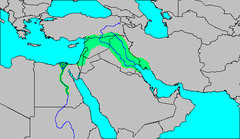
The fertile crescent
The land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers was called. Known as the Cradle of Civilization it is regarded as the birthplace of agriculture, urbanization, writing, trade, science, history and organized religion and was first populated c.10,000 BCE when agriculture and the domestication of animals began in the region.
sumerians
The people who dominated southern Mesopotamia through the end of the third millennium B.C.E. They were responsible for the creation of many fundamental elements of Mesopotamian culture-such as irrigation technology, cuneiform, and religious conceptions.
Egypt
In the early 19th century, the Ottoman Empire lost this North African country which had been part of it's empire. society was ruled by a pharaoh considered the incarnation of the sun god who controled acces to the Nile; they had hieroglyphics, the 365-day calender, they were polythestic and worshipped the dead
Hebrews
Early group of people who lived in lands between Mesopotamia and Egypt. They developed the religion Judaism.
A smaller early civilization whose development of a monotheistic faith that provided the foundation of modern Judaism, Christianity, and Islam assured them a significant place in world history
Phoenicians
located on eastern Mediterranean coast; invented the alphabet which used sounds rather than symbols like cuneiform
Persians
Ethnic group that settled in what is now Iran. They were rivals for control of Mesopotamia with the Greeks, and later the Arabs.
Minoans
The Mediterranean society that formed on the island of Crete and who were a big maritime society.
Mycenaean
a group of people who settled on the Greek mainland around 2000 B.C.; leading city called Mycenae which could withstand any attack; nobles lived in splendor; these people invaded many surrounding kingdoms
Polis
A city-state in ancient Greece.
Athens
This city was the seat of Greek art, science, and philosophy. Paul visited this city during his second missionary journey and spoke to the citizens about their altar to the unknown god.
Sparta
A powerful Greek miliary polis that was often at war with Athens. Used slaves known as helots to provide agricultural labor.
The Persian wars
A series of wars where the Greek city-states united against Persia, and managed to maintain control of the Aegean Sea and push the Persian Empire back
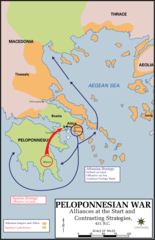
Peloponnesian war
(431-404 BCE) The war between Athens and Sparta that in which Sparta won, but left Greece as a whole weak and ready to fall to its neighbors to the north.
thirty tyrants
After Athens surrendered to Sparta at the end of the Peloponnesian war in 404, Sparta set up a government system in Athens which consisted of thirty tyrants. This system was very unpopular, and democracy was restored in Athens by 403